Role:
The most crucial function of a safety relay is to build a highly reliable safety control circuit. When its own or external equipment malfunctions, it can ensure that the system switches to a safe state (usually stop), thereby protecting the safety of personnel and equipment.
Unlike ordinary relays, safety relays are designed in accordance with the "fault safety" principle. This means that even if it has internal faults (such as contact adhesion, coil burnout, spring breakage, etc.), its output will be forcibly disconnected, causing the controlled equipment to stop running instead of dangerously continuing to operate.
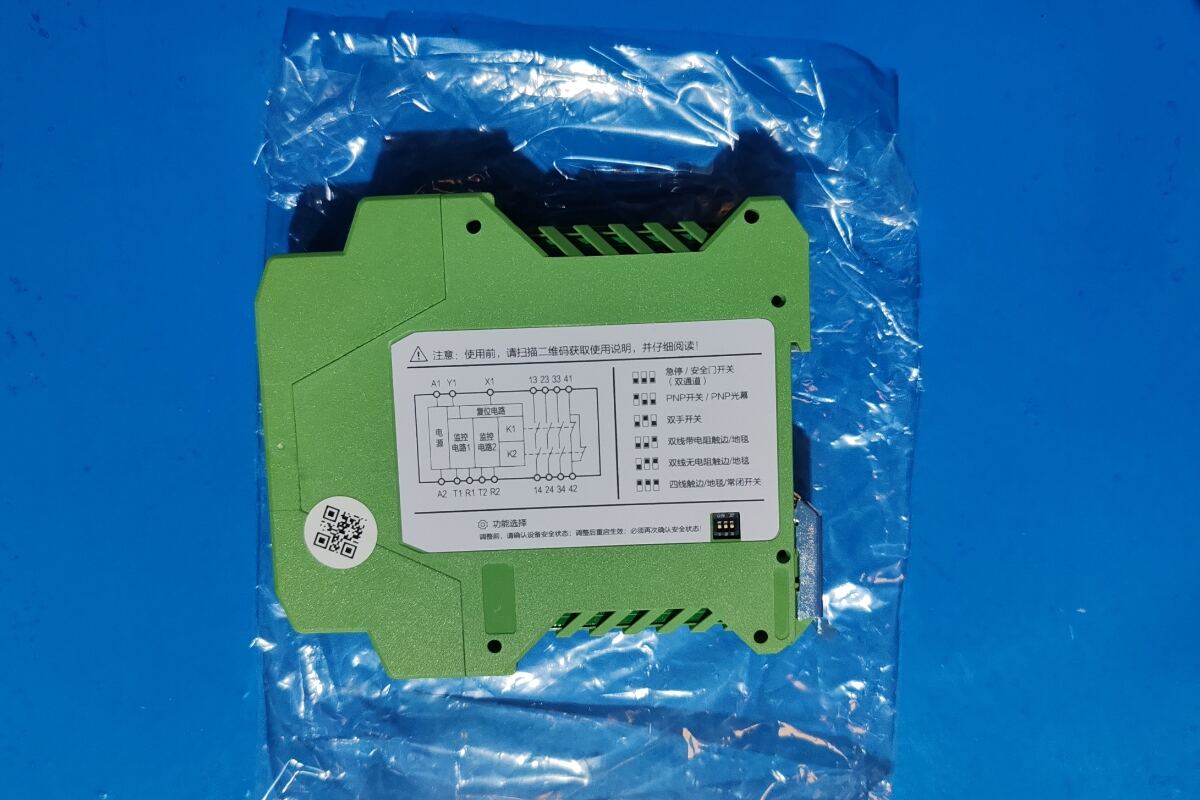
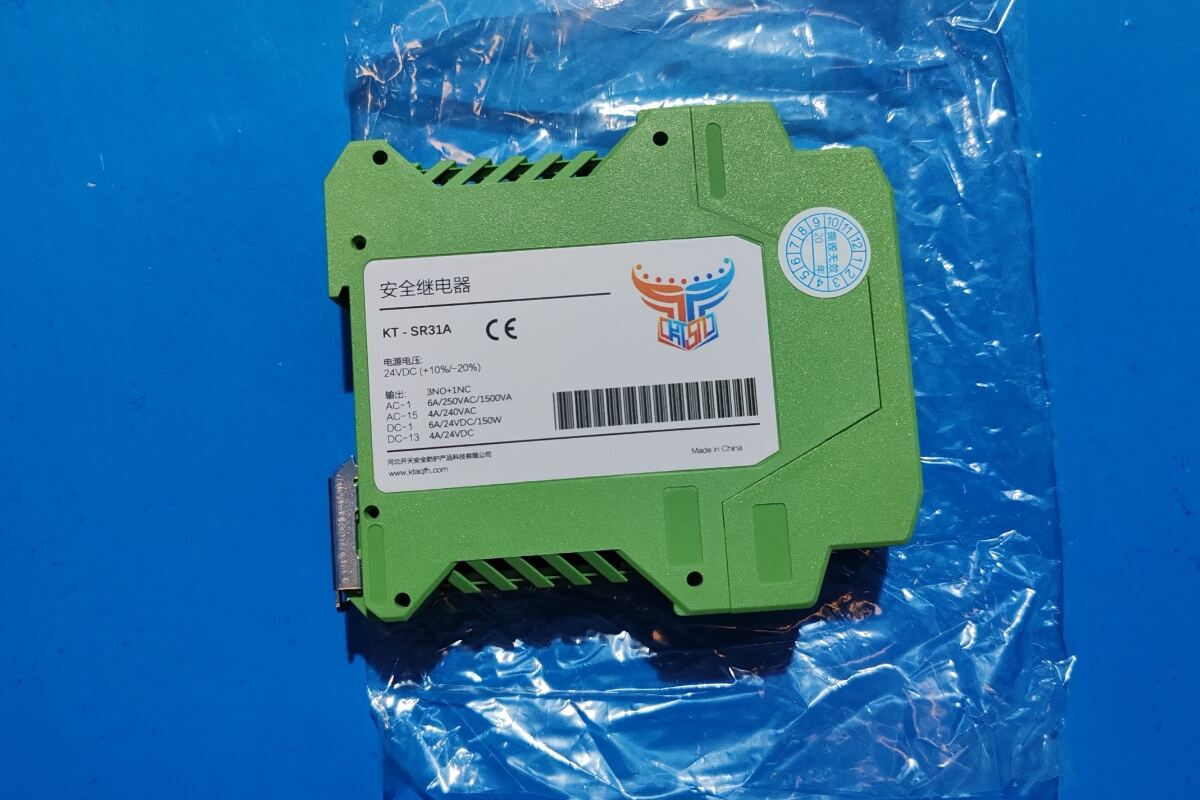



Main Functions:
1.Forced guidance contact structure
This is the most fundamental difference between safety relays and ordinary relays. It has a special mechanical interlocking structure inside, ensuring that the normally open contacts and the normally closed contacts cannot close simultaneously.
Working principle: When the coil is energized, the normally open contact closes and the normally closed contact opens. If the normally open contacts cannot be opened due to a fault (such as contact fusion welding), the internal mechanical interlock will prevent the normally closed contacts from closing. In this way, during safety checks (such as testing the circuit before resetting), the control system can identify faults by detecting that the normally closed contacts are not closed, thereby preventing the equipment from starting up.
Objective: To actively detect its own contact faults and prevent safety function failure caused by contact adhesion.
2.Redundancy and self-monitoring
Redundant design: There are usually two or three independent relay circuits inside a safety relay. They work together to jointly control the output. The final safety output will only be connected when all internal relays operate normally. If any of them malfunctions, the entire output will be cut off.
Self-monitoring: By monitoring the status of internal contacts (utilizing the principle of forced guidance) and the logical relationship of input signals, the safety relay can continuously diagnose itself. Once an anomaly is detected, it will immediately lock and cut off the output.
3.Dual-channel input
Most safety relays are designed with two independent input channels (for example, CH1 and CH2) for connecting safety devices such as emergency stop buttons, safety door switches, light curtains, etc.
4.Objective:
Short circuit detection: If a short circuit occurs between two input signal lines, the safety relay can detect it through logical judgment. For instance, when an emergency stop button is pressed, theoretically, both channels should be disconnected simultaneously. If only one is disconnected and the other remains "on" due to a short circuit, the relay will determine it as a fault and lock it.
Enhance reliability: Dual-channel provides redundancy. Even if one channel fails, the other channel can still trigger safety functions.
5.Reliable manual reset function
After the safety conditions are restored (for example, when the emergency stop button is reset or the safety door is closed), the safety relay will not automatically resume output. It must be manually reset through a separate and clear "Reset" button or signal.
Objective: To ensure that the operator must personally confirm the on-site safety status and proactively operate the reset before the equipment can be restarted. This prevents the device from accidentally restarting when the danger has not been eliminated.
6.Status indication
Safety relays are usually equipped with multiple LED indicator lights (such as power, input channel status, output status, fault status, etc.), which can quickly diagnose the system status and facilitate fault detection and maintenance.
 Hot News
Hot News2025-11-07
2025-10-22
2025-09-23
2025-02-24
2025-02-24
Copyright © 2025 Qinghe County Kaitian Safety Protection Technology Co.,ltd. All rights reserved. - Privacy policy